Loanable Funds
Essential Question: What factor has the biggest impact on the money supply, lending and investment?
- Interest Rates (the price of borrowing & using money)
Nominal v. Real Interest Rates
Nominal:
- Real interest rates + expected inflation
- % increase in money that the borrower pays including inflation
Real:
- Nominal interest rate - expected inflation
- % increase in purchasing power that the barrow pays (adjusted)
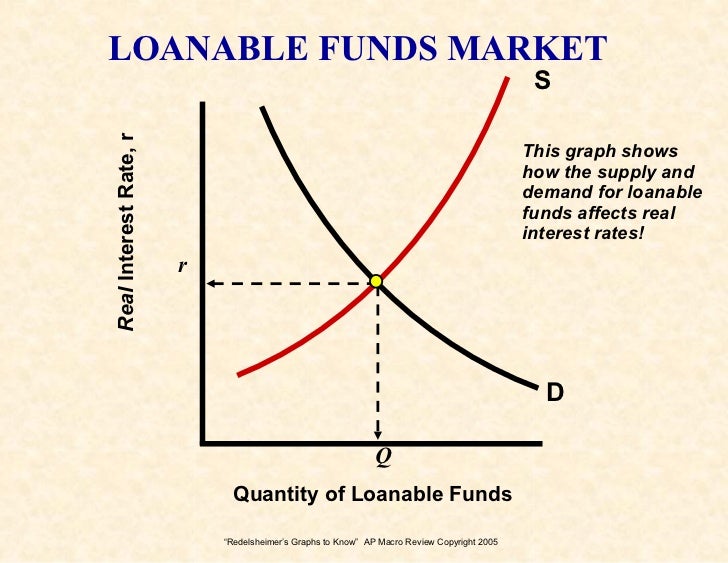
What are loanable funds?
-funds available for borrowing or lending
Demand for Loanable Funds
- the quantity of credit wanted and needed at every real interest rate by borrows in an economy
- Loanable Funds demand consists of any and all activities of borrowers who were credit, including: loan application and financial asses sales.
Demand for loanable funds?
- the quantity of credit wanted and needed at every real interest rate by borrowers in an economy
- Loanable funds demand - consists of any and all activities of borrowers who desire credit, including: loan application and financial asset sales.
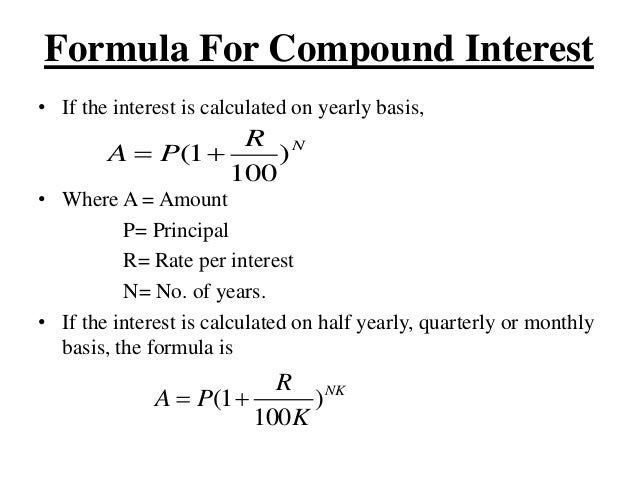
Time Value of Money
Is a dollar today worth more than a dollar tomorrow? YES
Why?
- inflation and opportunity cost
- this is the reason for charging and paying interest
Let V = future value of $.
P = present value of $.
r = real interest rate ( nominal rate - inflation expressed as a decimal)
n = years
k = # of times interest is credited per year
Demand Money
- has an inverse relationship between nominal interest rates and the quantity of money demanded
- quantity demanded falls because individuals would prefer to have interest earning assets instead of borrowed liabilities
What happens to quantity demand when interest rate decreases?
- quantity demanded increases.
- There is no incentive to convert cash into interest earning asset.
What happens if price level increase?
- then money demand shift to the right
3 Causes:
- change in price level
- change in income
- changes in taxation that affects investment
Increasing Money Supply
If the FED increases the money supply, a temporary surplus of money will occur at 5% interest.
- the surplus will cause interest rate to fall 2%
How does this affect AD?
Increase MS > Decrease interest rate > increase investment > Increase in AD
How do we decrease Money supply?
Decrease MS > Increase interest rate > decrease investment > decrease AD
Fiscal Sector
- Financial assets vs. Financial liability
- Assets: stocks or bonds that provide expected future benefit.
: benefits the owner only if the ensure of the asset need certain obligation
- Liability: it is incurred by the ensure of a financial asset to stand by the issue asset
: what you owe - Interest Rates: it is the price paid used for financial assets
- stock v. bonds
- stocks: financial asset that convey ownership in cooperation- bonds: promise to pay a certain amount of money
and interest in the future
What do Banks do?
A bank is financial intermediary
- uses liquid assets (i.e bond deposits) to finance the investment of borrowers
- Process is known as fractional reserve banking
- system in which depository institution liquid assets less than the amount of deposit
- can take the form of:
1. currency in bank vaults
2. bank reserves - deposits held at the Federal Reserve
Basic Accounting Review
- T-account (balance sheet)
- statements of assets and liabilities - Assets (amount owned)
- items to legal to which a bank holds legal claim
- the uses of funds by financial intermediates - Liabilities (amount owned )
- legal claim against a bank
Federal Reserve Bank
Function of FED:
- it issues paper money
it sets reserve requirement and it hold reserve of the bank
- lend money to bank and change their interest
-check clearing service for bank
-acts as a personal bank for government
- supervises member banks
- control money supply


No comments:
Post a Comment